Top Stories
A Parent’s Guide to Managing Diarrhea and Ear Infections in Nepal

The multi dimensional path through chronic pain: A deep dive into the hidden biology of recovery
Will a landmark judgment spur progress from menstrual hygiene to menstrual justice?

History in making as governments draft a legally binding Treaty for rights of older persons
Breaking the Black Box: How Artificial Embryos and Lab-Grown Wombs Are Unlocking the Secrets of Human Life
Editor's Picks
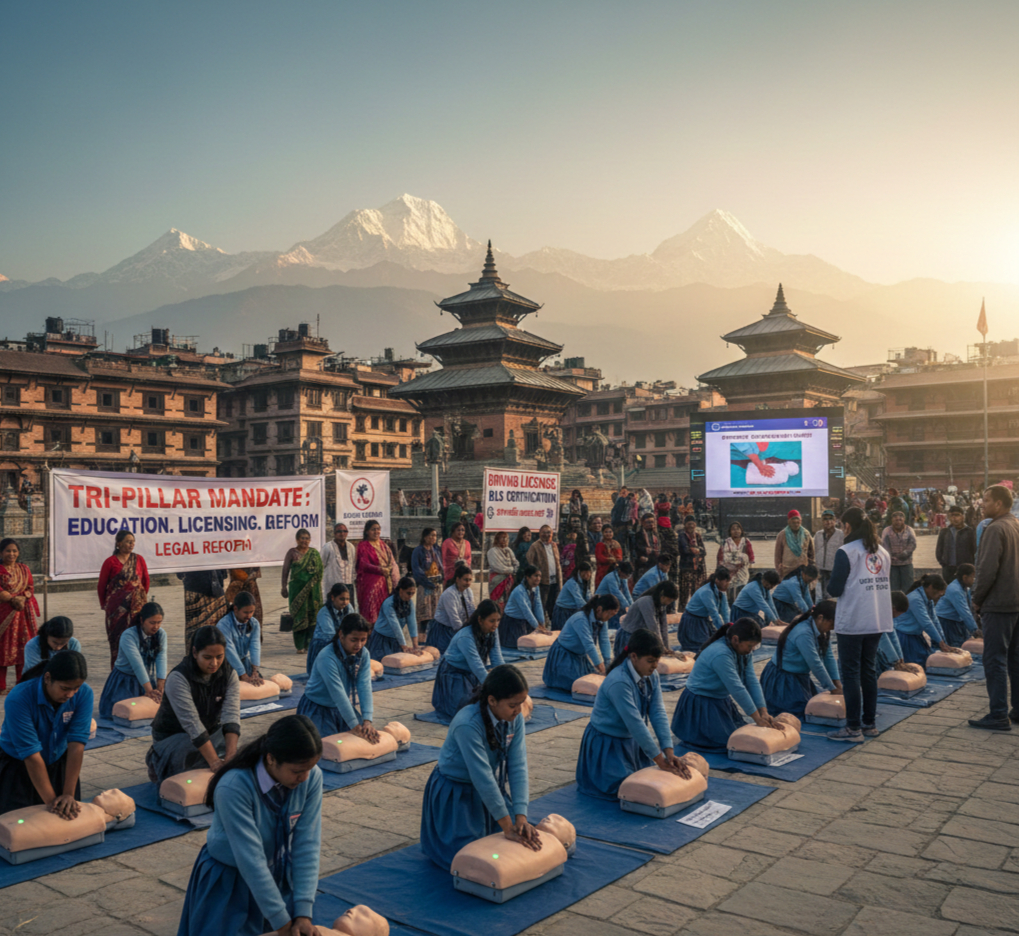

Policy Blueprint for Universal Basic Life Support Competency in Nepal: A Tri-Pillar Mandate
The health system of Nepal is actively engaged in strengthening its pre-hospital emergency medical services (EMS) through focused training of professionals, including Basic Emergency Medical Technicians (BEMTs) and community responders, often in coordination with international partners such as the W
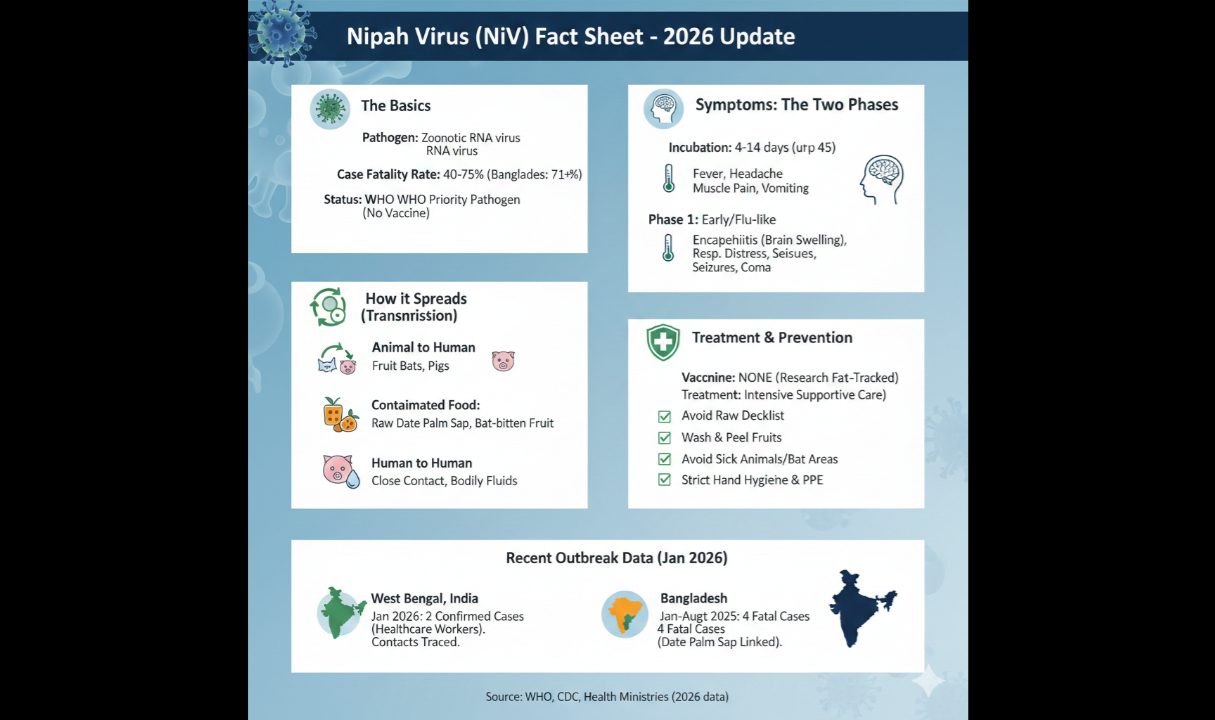
Nipah Virus: An Evolving Global Health Threat and the Path to Preparedness
Introduction The Nipah virus (NiV) represents one of the most significant viral threats to global health secur
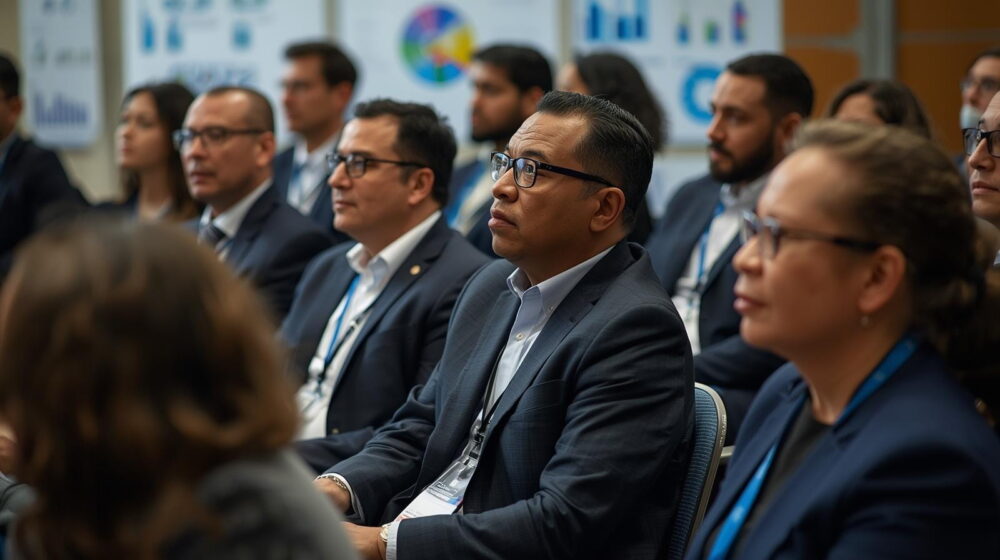

APCAT Summit unites local governments to save lives from tobacco, TB, AMR and NCDs
Written by Shobha Shukla (Managing Editor of CNS),Summit of sub-national government leaders from over 121 cities of 12 countries in Asia and the Pacific region unitedly passed an important declaration in Jakarta, Indonesia to save lives from preventable causes of diseases and untimely deaths, like tobacco use, TB, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and non-communicable diseases (NCDs). […]

Air Pollution in Kathmandu: Why the ‘Fluctuating’ AQI is a Silent Killer
Air Pollution in Kathmandu has reached a critical tipping point in January 2026. While the AQI fluctuates, TheHealth Thread breaks down the medical reality of this silent emergency and why the ‘improving’ numbers are more dangerous than they seem. This fluctuation is dangerous. It tricks us into th
Latest News
See all
The Chemistry of Feeling: Why Your Mood Starts in the Gut
We’ve all heard the phrase “you are what you eat,” but we rarely take it literally. Usually, we think of it in terms of waistlines or heart health. However, a growing body of research suggests that our diet is actually the primary architect of our emotional world—proving that your mood starts in th

Beyond the Bottleneck: A Blueprint for Sovereign Medicine Security in Nepal
Reviewed by Amrita Acharya, PhD Scholar (Pharmacy & Business Management) When a doctor in a rural health post in Karnali prescribes an antibiotic, they are acting on faith. Faith that the label matches the contents. Faith that the chemical structure hasn’t degraded in the heat. Faith that the regulatory system in Kathmandu has done its […]

Impacting positive change for those left behind
Written by Shobha Shukla (Managing Editor of CNS),Given the medical advancements today – in an ideal world, all children should be born free of infections like HIV, syphilis or hepatitis-B; all pregnant women should be accessing full spectrum of maternal and newborn care (including services to prevent vertical transmission of HIV, syphilis or hepatitis-B); and […]

Put people first mantra to drive WHO task force to save the medicines that protect us
Written by Shobha Shukla (Managing Editor of CNS),The United Nations apex health agency – the World Health Organization (WHO) – had announced the establishment of its first-ever civil society Task Force on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in October 2025. This marks a major shift in addressing AMR which is not only among the top 10 global […]
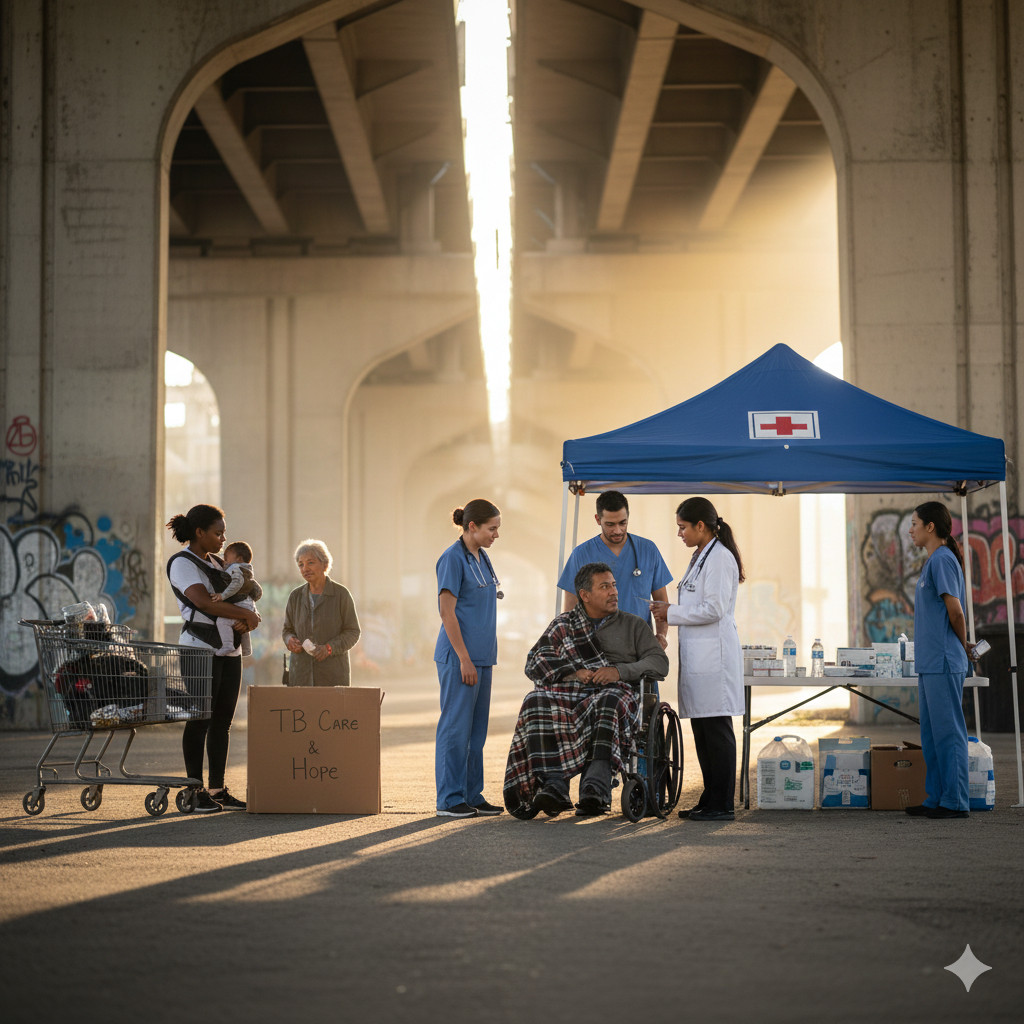

From shadow to light: Supporting unhoused persons to access lifesaving TB services
Written byShobha Shukla (Managing Editor of CNS),Bobby Ramakant (CNS Health Editor)The risk of getting TB disease is among the highest in unhoused and other marginalised persons but the likelihood of them seeking public TB services is low – and finishing lifesaving TB therapy is even lower. The delay is long – very long – for […]
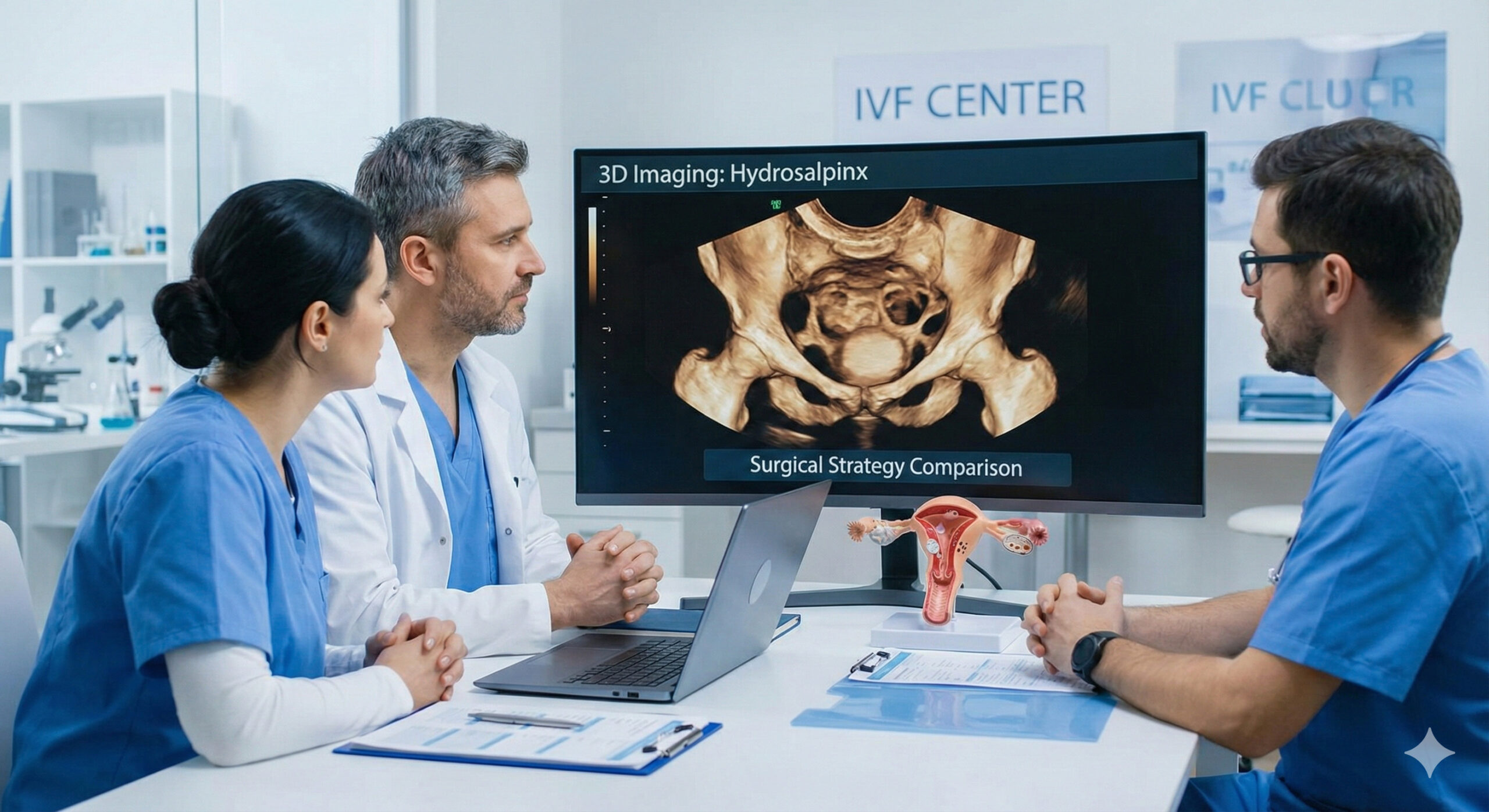
Advanced Clinical Analysis of Hydrosalpinx Management Before In Vitro Fertilization: Comparing Surgical Strategies and the Role of 3D Imaging Diagnostics
Reviewed byDr. Asmita Pandey, MD,Specialist in Obstetrics, Gynecology & ARTI. Executive Summary: The Necessity of Pre-IVF Hydrosalpinx Management The successful outcome of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) cycles is significantly impaired by the presence of hydrosalpinx (HS), a common pathology among women with tubal-factor infertility.1 Clinical data consistently demonstrate that HS reduces pregnancy, implantation, and ultimately, […]
Health News
See all
Nepal’s 40% Out of Pocket Health Burden

A Parent’s Guide to Managing Diarrhea and Ear Infections in Nepal

The multi dimensional path through chronic pain: A deep dive into the hidden biology of recovery

Will a landmark judgment spur progress from menstrual hygiene to menstrual justice?
History in making as governments draft a legally binding Treaty for rights of older persons
Wellness & Lifestyle
See all
Nipah Virus: An Evolving Global Health Threat and the Path to Preparedness

APCAT Summit unites local governments to save lives from tobacco, TB, AMR and NCDs

Air Pollution in Kathmandu: Why the ‘Fluctuating’ AQI is a Silent Killer

The Chemistry of Feeling: Why Your Mood Starts in the Gut

Beyond the Bottleneck: A Blueprint for Sovereign Medicine Security in Nepal
Research Watch
See allSilent Suffering: Why Nepal’s Doctors and Nurses Are Not Reporting Child Abuse
New Study Highlights Metabolism Risks in Combination Antidepressant Therapy in Nepal
New Study Reveals Hidden Environmental Drivers Behind Nepal’s Ongoing Cholera Battle
The Silent Pandemic: Kathmandu’s Poultry Industry Is Breeding Untreatable Superbugs
The Silent Emergency: Domestic Violence and the Mental Health Crisis Among Nepalese Women
Nepal’s Drug-Resistant TB Rates Hold Steady, but New Antibiotic Resistance Sparks Concern
Specialized Care
See all
From shadow to light: Supporting unhoused persons to access lifesaving TB services

Advanced Clinical Analysis of Hydrosalpinx Management Before In Vitro Fertilization: Comparing Surgical Strategies and the Role of 3D Imaging Diagnostics

Tobacco-free and nicotine-free future is a bedrock to deliver on #EndTB and SDGs

Zimbabwe and Cambodia getting return on investment by addressing AMR
Featured Story

Tobacco-free and nicotine-free future is a bedrock to deliver on #EndTB and SDGs
Written by Shobha Shukla (Managing Editor of CNS),According to the latest WHO Global TB Report 2025 released a week ago, tobacco smoking is among the top-5 risk factors for the deadliest of all infectious diseases worldwide – tuberculosis (TB). In countries with alarmingly high tobacco use, like Indonesia, tobacco use is the biggest risk factor […]
In Depth
Long Reads
Antibiotic resistance: A Global threat and an unseen pandemic

Skipping Breakfast, Missing Health: What Nepal’s Adolescents Are Really Eating

The Growing Crisis of Adolescent Obesity in Nepal : Causes, Consequences, and Solutions

Dietary Pattern and Nutritional Status among Healthcare Professionals
Quick Headlines
Gateway to universal access to SRHR is human right to health
World's largest TB prize illuminates Indian Molbio's tech innovation reaching the unreached
Amidst anti-gender push, hope pins on ICFP 2025 to shift gears towards SRHRJ for all
Study proves strong impact of taking molecular TB diagnostics closer to the people
Opinion & Analysis
Supporting and Educating Strategies for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
Introduction This article describes the meaning of Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD), the characteristics of ASD, the diagnosis process of ASD, ASD diagnosis instruments, and the strengths and interests of children with ASD. The article also presents supporting and educating techniques, behaviour man
Flaxseed: An Ancient Superfood for Today’s Health and Wellness
Plants have long been a cornerstone of traditional medicine and nutrition, with their bioactive components contributing significantly to their medicinal value. One such plant genus with notable bioactive phytochemicals is Linum usitatissimum , commonly known as flax. Flax is an ancient crop primari
Epistaxis
Nosebleeds, or epistaxis, are a common medical issue affecting approximately 60% of people in the United States at some point in their lives. Although most episodes are minor and self-limiting, around 6% of individuals experiencing nosebleeds will seek medical attention (Tunkel et al., 2020). In ch
Explore Health Topics
More Stories
See all
Zimbabwe and Cambodia getting return on investment by addressing AMR

Gateway to universal access to SRHR is human right to health

World's largest TB prize illuminates Indian Molbio's tech innovation reaching the unreached

Amidst anti-gender push, hope pins on ICFP 2025 to shift gears towards SRHRJ for all

Study proves strong impact of taking molecular TB diagnostics closer to the people

Rising Heat and Our Minds: The Overlooked Link Between Climate Change and Mental Health
Get The Health Thread delivered to your inbox
Join thousands of readers who start their week with our curated health news, research breakthroughs, and expert analysis. Free, every Monday.
No spam, ever. Unsubscribe anytime.
Latest Headlines
Antibiotic resistance: A Global threat and an unseen pandemic
Skipping Breakfast, Missing Health: What Nepal’s Adolescents Are Really Eating
The Growing Crisis of Adolescent Obesity in Nepal : Causes, Consequences, and Solutions
Dietary Pattern and Nutritional Status among Healthcare Professionals
Defective Sperm and Pregnancy Complications: Understanding the Connection and Its Impact
Supporting and Educating Strategies for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
Flaxseed: An Ancient Superfood for Today’s Health and Wellness
Epistaxis
Exploring the Role of Metabolic Psychiatry in Understanding Mental Health Disorders
Micro plastics: A Silent Threat to Reproductive Health and Fertility
Is Your Medicine Cabinet Missing This? Laughter’s Amazing Benefits
Advancing Kidney Health: Transforming Innovative Concepts into Practical Solutions
Chilies, is it only hot or more?
“Ethical Health Journalism, from Kathmandu to the World”
The Health Thread bridges the gap between complex medical research and everyday readers. Our team of certified journalists and medical reviewers ensure every article meets the highest standards of accuracy and ethics.